Services
Unsere umfangreiche Dienstleistungen für schweizweit zufriedene Kunden.
Consulting
We advise our clients in all areas of facility management, especially in the review of cleaning concepts in order to utilise synergies and exploit savings potential.
We bring our experience and expertise to bear in reviewing existing cleaning concepts, locating potential for improvement, developing detailed solutions and showing how costs can be saved for our customers. For the tendering of cleaning contracts, we optimise the process so that the offers of different applicants can be easily compared with each other.
Our consulting includes the following sequences
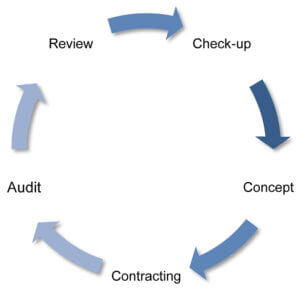
Check-up
The check-up records the initial situation and the deviation from the customer's requirements and possible potentials.
- Analyse needs, service level agreement (SLA), effective performance and costs.
- Verify the implementation of legal requirements, quality and environmental standards as well as occupational and corporate safety requirements
- Examine the organisation, competences, leadership, staff development and control
- Accompanying the awarding of contracts and improving logistics and purchasing
- Optimise interfaces and reporting
Concept
With the strength-weakness-profile we develop an individualized efficiency-oriented operating concept.
- Evaluation of the preferred strategy, objectives and concept variant
- Definition of quantity structures, service levels, methods, frequencies, order provisions, etc.
- Definition of important indicators (KPI), definition of reporting and cost structure
- Outline the training, logistics and monitoring concepts
Contracting
Our support of the procurement process brings clear and measurable specifications and guarantees cost transparency.
- Define the tendering process and selection criteria
- Preparation of the tender documents
- Evaluate the bids, draw up the shortlist and submit a contract proposal.
Audit
Our audit is intended to identify solutions for continuous improvement and thus make potentials usable.
- Identify deviations from the customer's needs and possibilities
- Motivation of the organisation for the solution and the goal orientation
- Identifying promotional measures among the stakeholders
Review
The review serves to reflect on what has been achieved and what still needs to be implemented.
- Recognition of sustainable promotion measures of the organization and the respective participants
- Benchmarking and market comparisons help to classify yourself
- Setting new goals and measures and reviewing them
Analysis example in the area of washroom hygiene
For our clients, we first analyse position by position to determine how high the costs for washroom hygiene are.
- the cost of consumables such as toilet paper, towel paper or towel rolls, hand soap, seat cleaner, etc.
- the costs for the necessary equipment, its control and filling
In our overall assessment, we make systems and products from different manufacturers comparable - for example by calculating the "consumption per operation". Based on the results, we can show which products are best suited in a specific case.
Calculation example washroom hygiene
In the 2nd step, we determine the break-even point for a system change for our customers. Our experience shows that costs can be reduced by around a fifth in the first year; the investment in new equipment pays off after just a few months. And that with higher quality hygiene equipment and products.
Improved operational hygiene at lower costs!
Bronze, Silver, Gold and Platinum Services
Bronze

Basic performance
- Consulting
- FS-Shop access
- Delivery from 500.-
- Empty container transport
From 1st order
Silver

Operational Support
Bronze benefits +- Create flows (SVG)
- On-site instruction
- Products Training
- ASI - Tips
- System maintenance
Turnover > 10'000.00 CHF/year
Gold

Leadership Support
Silver benefits +
- Dosing technology installation
- Warehousing
- Environmental balance
- Training (1/2 day, 3 participants)
Turnover > 40'000.00 CHF/year
Platinum

System Support
Gold advantages +- Manual (SVG)
- Audit
- Microbiology, swab, water sample
- Further training (1 day/year for 3 participants)
After consultation
Training
Know-how and experience are decisive factors for success in the cleaning business, an industry that has undergone constant change in recent years. Increased hygiene requirements, higher cleaning standards and optimised processes demand economic concepts. This development demands profound knowledge from specialists and managers.
In individual courses on site or in the FM Academy at our headquarters, our customers receive practice-oriented expertise. This saves time and costs, reduces damage and accidents and is above all motivating for all employees.
We would be pleased to prepare a non-binding proposal for you or to guide you through our FM Academy, where you can get an overview of our current course offerings.
Tutorials
Our video tutorials provide you with an overview of our products and application possibilities. For answers to your questions or for an individual recommendation, please contact your KWZ consultant directly.
Historical area
Development Lab
We are constantly developing our products in our own analytical laboratory. In this way, we meet customer requirements, new laws and regulations, and our striving for more ecology. In addition, the consistently high product quality is ensured here.




Application technology
KWZ products are coordinated in such a way that sustainable and economical results can be achieved. Be inspired by our well thought-out cleaning systems! We regularly test our own products, machines and equipment for function and value retention and offer material tests in the course of construction projects and damage events.

Events
In order to give our customers from all over Switzerland access to new networks, ideas and further training, we held two KWZ seminars in 2020. We combined the baths and facility seminar so that the exchange of ideas and thoughts could be even more intensive. The positive feedback from participants has motivated us to hold further seminars.
Unfortunately, the events planned for 2021 have to be cancelled.
We are already looking forward to the seminars in 2022 which are planned as follows:
- Wednesday, 19.01.2022 - Thursday, 20.01.2022
- Wednesday, 26.01.2022 - Thursday, 27.01.2022
Glossary / Abbreviations
Check-off sample: Pressing a solid culture medium onto a surface to record the qualitative and quantitative microbial colonisation.
Abrasion test: A standardized area of 10×10 cm within an appropriate frame is swabbed with a moist swab. The swab is soaked with a special solution. In the laboratory, the colony-forming units (CFU) can then be determined using proven microbiological methods, usually the aerobic, mesophilic germs.
Adsorption: Physical binding of gases, vapours or dissolved substances to the surface of a solid body.
Aerobic, mesophilic germs (AMK): Aerobic, mesophilic germs are controlled in the water of artificial swimming and bathing pools or on surfaces. They are a measure of the presence of conditions conducive to proliferation.
ATP: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a very energy-rich compound, a kind of universal "energy currency" in the cell. It is found in all cells, of animal and plant origin. This also applies to bacterial, yeast and mould cells. Exceptions to this are viruses.
Basic Chlorination: Minimum concentration of free chlorine in the pure water (compensation of the free chlorine eliminated in the treatment).
BBL Contact Slide: Culture medium for the microbial count of bacteria, yeasts and moulds on surfaces.
Pool water: Water in swimming and bathing pools
Resources: Goods that do not belong to the building but are a prerequisite for its use and, unlike consumables, must be maintained and serviced or repaired. This includes equipment for the user such as sports equipment, swimming aids, laundry/textiles, dirt locks and work equipment such as high-pressure cleaners, cleaning equipment and tools.
Operational Chlorination: Chlorination dependent on bathing operation
MBioluminescence: ethode for checking the cleanliness of surfaces. In this process, the content of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is measured by defined procedures with special chemicals via a light-producing reaction. ATP is found in all living microorganisms. The procedure can be carried out on site and provides immediate results.
CAFM: Computer Aided Facility Management: Computer-aided FM. The functionalities of such systems vary. Common features are a CAD interface in which building plans can be edited and enriched with information and a database that supports order management, ticketing and quality management. More recently, these solutions are web-based and also have an APP.
Disinfection: Targeted reduction of the number of certain undesirable microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, mycobacteria, viruses) by physical or chemical, irreversible inactivation, so that they can no longer cause infection under the given circumstances and undesirable biofilm formation is contained.
Disinfectant: Chemical substances or mixtures of substances that kill or inactivate microorganisms on surfaces, in liquids or gases.
eBKP: Electronic construction cost plan in which, among other things, all technical systems are listed in a tree structure and can be used for system inventory and maintenance planning.
First filtrate: Filtrate immediately after filter flushing until the actual filter function is restored.
Escherichia coli (E. coli): Bacteria which serve as faecal indicators. They are an indication of contamination of the water by intestinal germs.
Filtrate: Filtered water before adding the disinfectant.
fKH: Carbonate hardness in French hardness grades.
Surface disinfection: Disinfection of inanimate surfaces such as floors, inventory, equipment, etc. (spray disinfection, wipe disinfection, scrub disinfection). (spray disinfection, wipe disinfection, scrub disinfection)
FNU/NTU: FNU - "Formazine Nephelometric Units": Unit used in water treatment for measurement at 90° in accordance with the provisions of the ISO 7027 standard - Nephelometric Turbidity Unit.
Freeboard: Distance between the top edge of the inlet/outlet device and the top edge of the filter layer.
Fresh water: For initial filling and replenishment of used water.
Bound Chlorine: Undesirable disinfection by-product (DNP). The free chlorine oxidizes (burns) organic substances. A preliminary stage of complete oxidation is the binding of chlorine to amine (contained in proteins). The resulting chloramine is called combined chlorine. Chloramine has an irritating effect and causes the so-called indoor swimming pool smell. Calculation: Total chlorine minus free chlorine.
Shared bathrooms: Publicly accessible facility or bath: a facility or bath open to the general public or to an authorized group of persons and not intended for use in a family setting.
(Ordinance of the FDHA on Drinking Water and Water in Publicly Accessible Baths and Shower Facilities (TBDV)
Hygiene: The study of the preservation and maintenance of health. In maintenance, it concerns the measures that help prevent the transmission of infectious diseases.
KBE: Colony-forming units. A parameter of bacteriological examination for the quantitative detection of microorganisms capable of living and reproducing. It indicates how many colonies are visible at a 6- to 8-fold magnification on a defined culture medium after a certain incubation period and certain incubation time. Accordingly, the colony count can contain additional information about the degree of contamination of a water, surfaces or objects.
KMnO4: Potassium permanganate: Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidizing agent, i.e. it tends to give up its oxygen, which it has right in the quad, to organic compounds. It is a method of testing clean, or slightly polluted water, such as pool water represents. Dirt "eats up" potassium permanganate, so to speak. 2 mg of dirt "eats up" 2 mg of potassium permanganate. If we add 10 mg of potassium permanganate to one litre of pool water and 5 mg of KMnO4 remains after the sample, then we detect 5 mg of dirt per litre of pool water. This corresponds to the quality target.
Level of contamination: Degree of contamination and/or load.
Legionella: Bacteria which occur in humid biotopes. Infections (pneumonia) occur through inhalation of droplets containing the pathogen (aerosol). Possible sources of infection are: Hot water systems (showers), humidifiers, bubble baths.
Machinery Directive: Legal requirement EN 2006/42/EC for the prevention of accidents. Commercially used machines must comply with the standard. Household machines do not meet the requirements.
N.N.: Undetectable.
OdA igba: OdA Bathing and Ice Sports Facilities:
Interest group for the professional training of bathing and ice sports facilities.
Oxidation: Chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from the substance to be oxidised (electron donor) to the oxidising agent (electron acceptor). This in turn is reduced by the electron acceptance (reduction). Oxidation is mainly used for the disinfection and degradation of organic substances.
Oxidizability: KMnO4- Consumption
PC Agar: Nutrient medium for smear test pH value: Measure of the hydrogen ion concentration contained in aqueous solutions and thus a measure of the acidic, neutral or basic reaction of a solution. Acids have a pH value less than () 7. Water in its original form has a pH value of 7 (neutral).
Personal water area a: Water area (m2) allocated to a person by calculation
Person frequency n: Number of changes of persons per hour (h-1).
pH: The pH value is a measure of the acidic or basic character of an aqueous solution. This indicates the hydrogen ion activity and is derived from the Neo-Latin potentia Hydrogenii.
pH value = 0 - 4.0, acidic range = red label
pH value = 5.0 - 8.0, neutral range = green label
pH value = 9.0 - 14, alkaline range = blue label
pH-value - tolerances +/- 0.2 - 1.0 powder/granules i.R. 10%ige solution
PSA: The collective term PPE covers all products that protect people from occupational accidents and diseases while performing their occupational activities, such as boots, gloves, aprons, face and eye protection. They are sensibly used when the hazard cannot be eliminated or can only be eliminated inadequately by technical and/or organisational measures.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Generally, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is found where there is enough moisture, e.g. in washbasins, showers, floor drains, sauna dipping pools, etc.
In case of poor cleanliness, the bacterium can cause infections.
Cleaning Textiles: Mop and cloths for cleaning.
Pure water: Treated water after adding the disinfectant.
Guideline: Value to aim for.
RLU: Relative light unit.
Rodac plates: Replicate organism detection and counting, nutrient medium for smear test, ready-mixed nutrient media cast in special plates. The culture media or the plates are coated or filled with nutrient agar in such a way that the agar layer protrudes over the edge (convex surface).
Raw water: Water fed to the treatment plant.
Muddy water: Water produced during the rinsing of filters.
Dirt: Matter in the wrong place.
Gushing water: The overflowing volume flow and the displacement water by bathers.
Swimming or bathing pool: Continuously flowing water basin in which one or more people are present at the same time or in chronological succession as intended.
Swimming or bathing pool facility: The entirety of the pools, their equipment and the structural and technical installations for the treatment of the swimming or bathing pool water.
SIA: Swiss Association of Engineers and Architects: www.sia.ch
Sorption: Generic term for adsorption and absorption (absorption of foreign molecules by liquids and solids).
Rinse water: Water used for rinsing filters.
Malfunction: An exceptional occurrence in an establishment in which significant impacts occur outside the premises of the establishment.
SVG: Swiss Association for Health Protection and Environmental Technology
Tolerance value: Value below or above which (in the case of range specifications: outside the range) a reduced water quality is present. Measures are to be taken.
TPC: Nutrient medium for the smear test. The most frequently occurring bacteria, yeasts and fungi grow on this culture medium. It is therefore used to determine the total bacterial count. Fields of application e.g.: general surfaces, devices, persons, liquids.
Overflow water: Water constantly draining over the edge of the pool.
Consumables: Goods that do not belong to the building, but are a prerequisite for its operation and must be continuously replenished. This includes all media such as water, heating oil and natural gas, cleaning agents and disinfectants, lubricants, brine, oils and aerosols.
Water Hardness: The content of calcium ions (Ca2+) and magnesium ions (Mg2+) in a water.
Water hardness is given in millimoles per litre (number of calcium and magnesium particles per litre of water) or in French degrees of hardness °fH and is divided into six hardness levels. Alternatively, the water hardness is given in German degrees of hardness °dH and is divided into three hardness levels. Conversion: 10 °fH= 5.6 °dH.
Water hardness table
| Total hardness °fH | Total hardness mmol/l | Designation |
| 0 to 7 | 0 to 7 | 0 to 7 |
| >7 to 15 | >0.7 to 1.5 | soft |
| >15 to 25 | >1.5 to 2.5 | medium hard |
| >25 to 32 | >2.5 to 3.2 | quite hard |
| >32 to 42 | >3.2 to 4.2 | hard |
| > 42 | >4.2 | very tough |
| Total hardness °dH | Total hardness mmol/l | Designation |
| 0 to 8.4 | 0 to 1.5 | very soft |
| >8.4 to 14 | >1.5 to 2.5 | soft |
| >14 | >2.5 | medium hard |
Subscribe to Newsletter
Company
Management system
















